DUMAS complete nitrogen / protein determination device
Velp Scientifica
Request a price
Automatic nitrogen / protein determination based on the Dumas method.
The method does NOT require wet chemical preparation! It does not produce hazardous waste that cannot be treated in liters. Really environmentally friendly technology.
The device can be equipped with an automatic sample changer that can be expanded to 117 places, and thanks to the DUMASoft PC software included with the device, it does NOT require the continuous presence of the analyst. It can even work independently at night. An analysis of approx. It takes 3-4 minutes, so you can measure the 117 samples within 8 hours (e.g. during night work).
With the CN 802 type device, in addition to nitrogen, the carbon content can also be determined, this analyzer is available on the following page.
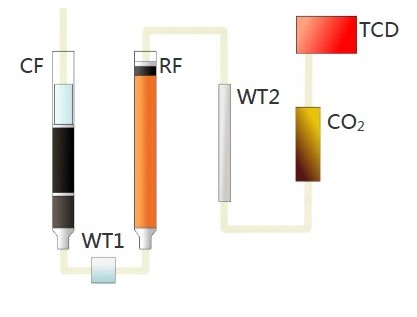
Technical data of the NDA 702 Helium carrier gas version:
| NDA 702 with He carrier gas | |
|---|---|
| Sensor: | TCD sensor with automatic calibration |
| Maximum sample weight: | 1 g |
| Automatic sample changer capacity: | 4 discs with 30 positions each (supplied with 1 disc) |
| Repeatability (RSD): | < 0.5% (for EDTA standards, 9.57%N) Recovery: > 99.5% |
| Detection limit: | 0.001 mg nitrogen |
| Measuring range: | 0.1 - 200 mg of nitrogen |
Required gases:
- Helium (He): 99.999%, purity (grade 5.0) / 2 bar
- Oxygen (O2): 99.999%, purity (grade 5.0) / 2.5 bar
- Compressed air or nitrogen (N2): 99.6 %, purity (oil and water free) /3 bar
Other technical data:
| NDA 702 other technical data | |
|---|---|
| Data connection: | USB; RS232 port, computer control and analysis |
| Consumption: | 1,400 W |
| Dimensions (W x H x D): | 655x510x410 mm (H: 690 mm with autosampler) |
| Weight: | 54 kg |
Delivery includes: device, automatic sample changer with 1 disc, consumables kit for 1,000 measurements, DUMASoft PC software, USB and RS-232 cable. The computer is provided by the user!
NDA 702 can use two carrier gases. Since Helium is very expensive, so where the use of Argon is permissible, it will be economical to use this carrier gas.
The detection limit of the device will be 0.01 mg Nitrogen in Argon carrier gas mode.
The gas connection of the NDA 702 should be designed in such a way that the appropriate gas can be used as needed - by closing one tap and opening another.
Official procedures for food industry use:
| Industry | Official procedure | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Food | AOCS Ba 4e-93 | General combustion method for determining crude protein |
| Cereals, pasta, oilseeds, plants and nuts | AOAC 992.23 | Determination of crude protein in cereal grains by the general burning method |
| AACC 46-30 | Determination of crude protein by the burning method - flours, cereal grains, oilseeds, fodder | |
| ISO 16634-1:2008 | Determination of total nitrogen content by combustion according to the Dumas principle and calculation of crude protein content. Part 1: Oilseeds and fodder | |
| ISO/TS 16634-2:2009 | Determination of total nitrogen content by burning according to the Dumas principle and calculation of crude protein content. Part 2: Cereals, pulses and cereal flours | |
| ICC 167 | International Association for Cereal Chemistry (ICC). Determination of crude protein in grain, feed and food industry grain products by burning according to the Dumas principle. | |
| Barley | ASBC Barley 7C | American Society of Brewing Chemists (ASBC). Determination of crude protein in barley. |
| Soy | AOCS Ba 4f-00 | Determination of crude protein in soy flour using the combustion method. |
| Meat and meat products | AOAC 992.15 | Determination of crude protein in meat, meat products, and pet food. |
| Beer and must | ASBC AOAC 997.09 | Determination of nitrogen in beer, mash and beer dregs using a calculation method. |
| Milk and dairy products (cheese, milk powder, probiotics, drinks, yogurt, butter) | UNI EN ISO 14891, (FIL-IDF 185, 2008) | Determination of the nitrogen content of milk and diary products using the routine combustion method based on the Dumas principle. |
| Wine | OIV-MA-AS323-02A | Determination of total nitrogen according to the type II method of the Dumas method (musts and wines). |
Official procedures for feed industry use:
| Industry | Official procedure | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Fodder and pet food | AOAC 990.03 | Determination of crude protein in animal feed using the combustion method. |
Official procedures for agricultural use:
| Industry: | Official procedure | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Fertilizers | AOAC 993.13 | Determination of total nitrogen content in fertilizers. |
Official procedures for environmental use:
| Industry | Official procedure | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Soil, sludge, organic waste | ISO 13878:1998 | Soil analysis - Determination of total nitrogen content by dry burning ("elemental analysis") |
| EN 16168: 2012 | Sludge, treated biowaste and soil. - Determination of total nitrogen content using the dry combustion method. |
Official procedures for chemical use
| Industry | Official procedure | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cellulose nitrate | STANAG No. 4178 | Military Standardization Agreement. Determination of nitrogen in cellulose nitrate by combustion according to the Dumas principle. |
| Tire (ABS, SAN) | ISO TC 45/SC 2 N2 116 | For the use of raw materials (including latex) in the rubber industry. Determination of the nitrogen content of raw materials, rubber and latex using the Dumas combustion method. |
| Motor oils | ISO 22241-2 | Diesel engines. NOx-reducing AUS 32 additive. Part 2: Test methods |
related products
With a 20-place sample changer and a sample weight of up to 5 g, the ELTRA TGA analyzer offers a convenient and fast alternative for analyzing the mass change of materials due to heat. Maximum temperature 1000 °C temperature.
More informationsDetermination of oxygen, nitrogen and hydrogen with a single device
More informationsComputer-controlled, resistance-heated, tubular furnace CS analyzer
More informationsDevice suitable for determining carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur and oxygen.
More informations